中文名稱(chēng):兔抗C7多克隆抗體
|
Background: |
The complement cascade is a multi-protein system that functions to clear pathogens from an infected host. Part of the innate (unchanging) immune system, the complement cascade consists of proteins and inactive zymogens that are present in blood and are stimulated by one of several triggers. Once stimulated, the cascade relays amplified responses throughout the body, ultimately activating the cell-killing membrane attack complex which can insert itself into the cell membrane and cause the cell to lyse. C7 (complement component 7) is an 843 amino acid secreted protein that participates in the formation of membrane attack complex (MAC), a complex that forms pores in the plasma membrane of target cells for innate and adaptive immune responses. As a membrane anchor, C7 exists as a monomer or dimer and can form multimeric rosettes with C5β. C7 defects are the cause of component C7 deficiency (C7D), characterized by recurrent bacterial infections caused by Neisseria meningitidis. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, WB |
|
Name of antibody: |
C7 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human C7 |
|
Full name: |
complement component 7 |
|
SwissProt: |
P10643 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
5000-10000 |
|
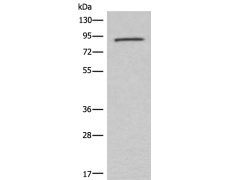
WB Predicted band size: |
94 kDa |
|
WB Positive control: |
HUVEC cell lysate |
|
WB Recommended dilution: |
500-2000 |

 購(gòu)物車(chē)
購(gòu)物車(chē) 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009